영상처리 이용한 image_alignment
개요
큰비젼 황태현 이사 교육 내용
#0 OpenCV 관련 설정
실행 화면
프로그램 설명
이미지 짤라서 정렬하는 함수인 warpAffine 에 대해서 알아보자
이 프로그램은 이미지 정렬을 사용하는것을 증명하는 프로그랩입니다.
This file demonstrates the use of the ECC image alignment algorithm.
이미지가 주어주면 램덤하게 자를수 있게 주어집니다.
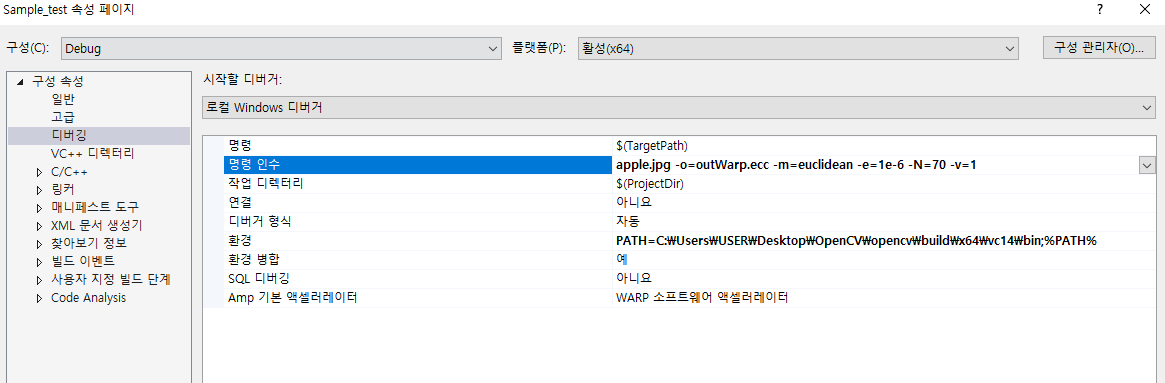
인자 값으로는 ex)apple.jpg -o=outWarp.ecc -m=euclidean -e=1e-6 -N=70 -v=1
- 입력 사진
- (옵션) 템플릿 파일 이름
- (옵션) warp(휨,또는 경사, 자르는 이미지?)
- -n ECC’s iterations
- -e ECC’s convergence epsilon
- -o 결과 파일명
- -m motion 종류 (translation, euclidean, affine, homography)
- -v 파일 갯수
- -9 경사 이미지
전체 코드
/*
* This sample demonstrates the use of the function
* findTransformECC that implements the image alignment ECC algorithm
*
*
* The demo loads an image (defaults to fruits.jpg) and it artificially creates
* a template image based on the given motion type. When two images are given,
* the first image is the input image and the second one defines the template image.
* In the latter case, you can also parse the warp's initialization.
*
* Input and output warp files consist of the raw warp (transform) elements
*
* Authors: G. Evangelidis, INRIA, Grenoble, France
* M. Asbach, Fraunhofer IAIS, St. Augustin, Germany
*/
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/video.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/utility.hpp>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
static void help(const char** argv);
static int readWarp(string iFilename, Mat& warp, int motionType);
static int saveWarp(string fileName, const Mat& warp, int motionType);
static void draw_warped_roi(Mat& image, const int width, const int height, Mat& W);
#define HOMO_VECTOR(H, x, y)\
H.at<float>(0,0) = (float)(x);\
H.at<float>(1,0) = (float)(y);\
H.at<float>(2,0) = 1.;
#define GET_HOMO_VALUES(X, x, y)\
(x) = static_cast<float> (X.at<float>(0,0)/X.at<float>(2,0));\
(y) = static_cast<float> (X.at<float>(1,0)/X.at<float>(2,0));
const std::string keys =
"{@inputImage | fruits.jpg | input image filename }"
"{@templateImage | | template image filename (optional)}"
"{@inputWarp | | input warp (matrix) filename (optional)}"
"{n numOfIter | 50 | ECC's iterations }"
"{e epsilon | 0.0001 | ECC's convergence epsilon }"
"{o outputWarp | outWarp.ecc | output warp (matrix) filename }"
"{m motionType | affine | type of motion (translation, euclidean, affine, homography) }"
"{v verbose | 1 | display initial and final images }"
"{w warpedImfile | warpedECC.png | warped input image }"
"{h help | | print help message }"
;
static void help(const char** argv)
{
cout << "\nThis file demonstrates the use of the ECC image alignment algorithm. When one image"
" is given, the template image is artificially formed by a random warp. When both images"
" are given, the initialization of the warp by command line parsing is possible. "
"If inputWarp is missing, the identity transformation initializes the algorithm. \n" << endl;
cout << "\nUsage example (one image): \n"
<< argv[0]
<< " fruits.jpg -o=outWarp.ecc "
"-m=euclidean -e=1e-6 -N=70 -v=1 \n" << endl;
cout << "\nUsage example (two images with initialization): \n"
<< argv[0]
<< " yourInput.png yourTemplate.png "
"yourInitialWarp.ecc -o=outWarp.ecc -m=homography -e=1e-6 -N=70 -v=1 -w=yourFinalImage.png \n" << endl;
}
static int readWarp(string iFilename, Mat& warp, int motionType) {
// it reads from file a specific number of raw values:
// 9 values for homography, 6 otherwise
CV_Assert(warp.type() == CV_32FC1);
int numOfElements;
if (motionType == MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY)
numOfElements = 9;
else
numOfElements = 6;
int i;
int ret_value;
ifstream myfile(iFilename.c_str());
if (myfile.is_open()) {
float* matPtr = warp.ptr<float>(0);
for (i = 0; i < numOfElements; i++) {
myfile >> matPtr[i];
}
ret_value = 1;
}
else {
cout << "Unable to open file " << iFilename.c_str() << endl;
ret_value = 0;
}
return ret_value;
}
static int saveWarp(string fileName, const Mat& warp, int motionType)
{
// it saves the raw matrix elements in a file
CV_Assert(warp.type() == CV_32FC1);
const float* matPtr = warp.ptr<float>(0);
int ret_value;
ofstream outfile(fileName.c_str());
if (!outfile) {
cerr << "error in saving "
<< "Couldn't open file '" << fileName.c_str() << "'!" << endl;
ret_value = 0;
}
else {//save the warp's elements
outfile << matPtr[0] << " " << matPtr[1] << " " << matPtr[2] << endl;
outfile << matPtr[3] << " " << matPtr[4] << " " << matPtr[5] << endl;
if (motionType == MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY) {
outfile << matPtr[6] << " " << matPtr[7] << " " << matPtr[8] << endl;
}
ret_value = 1;
}
return ret_value;
}
static void draw_warped_roi(Mat& image, const int width, const int height, Mat& W)
{
Point2f top_left, top_right, bottom_left, bottom_right;
Mat H = Mat(3, 1, CV_32F);
Mat U = Mat(3, 1, CV_32F);
Mat warp_mat = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_32F);
for (int y = 0; y < W.rows; y++)
for (int x = 0; x < W.cols; x++)
warp_mat.at<float>(y, x) = W.at<float>(y, x);
//warp the corners of rectangle
// top-left
HOMO_VECTOR(H, 1, 1);
gemm(warp_mat, H, 1, 0, 0, U);
GET_HOMO_VALUES(U, top_left.x, top_left.y);
// top-right
HOMO_VECTOR(H, width, 1);
gemm(warp_mat, H, 1, 0, 0, U);
GET_HOMO_VALUES(U, top_right.x, top_right.y);
// bottom-left
HOMO_VECTOR(H, 1, height);
gemm(warp_mat, H, 1, 0, 0, U);
GET_HOMO_VALUES(U, bottom_left.x, bottom_left.y);
// bottom-right
HOMO_VECTOR(H, width, height);
gemm(warp_mat, H, 1, 0, 0, U);
GET_HOMO_VALUES(U, bottom_right.x, bottom_right.y);
// draw the warped perimeter
line(image, top_left, top_right, Scalar(255));
line(image, top_right, bottom_right, Scalar(255));
line(image, bottom_right, bottom_left, Scalar(255));
line(image, bottom_left, top_left, Scalar(255));
}
int main(const int argc, const char* argv[])
{
CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, keys);
parser.about("ECC demo");
parser.printMessage();
help(argv);
string imgFile = parser.get<string>(0);
string tempImgFile = parser.get<string>(1);
string inWarpFile = parser.get<string>(2);
int number_of_iterations = parser.get<int>("n");
double termination_eps = parser.get<double>("e");
string warpType = parser.get<string>("m");
int verbose = parser.get<int>("v");
string finalWarp = parser.get<string>("o");
string warpedImFile = parser.get<string>("w");
if (!parser.check())
{
parser.printErrors();
return -1;
}
if (!(warpType == "translation" || warpType == "euclidean"
|| warpType == "affine" || warpType == "homography"))
{
cerr << "Invalid motion transformation" << endl;
return -1;
}
int mode_temp;
if (warpType == "translation")
mode_temp = MOTION_TRANSLATION;
else if (warpType == "euclidean")
mode_temp = MOTION_EUCLIDEAN;
else if (warpType == "affine")
mode_temp = MOTION_AFFINE;
else
mode_temp = MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY;
Mat inputImage = imread(samples::findFile(imgFile), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (inputImage.empty())
{
cerr << "Unable to load the inputImage" << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat target_image;
Mat template_image;
if (tempImgFile != "") {
inputImage.copyTo(target_image);
template_image = imread(samples::findFile(tempImgFile), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (template_image.empty()) {
cerr << "Unable to load the template image" << endl;
return -1;
}
}
else { //apply random warp to input image
resize(inputImage, target_image, Size(216, 216), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR_EXACT);
Mat warpGround;
RNG rng(getTickCount());
double angle;
switch (mode_temp) {
case MOTION_TRANSLATION:
warpGround = (Mat_<float>(2, 3) << 1, 0, (rng.uniform(10.f, 20.f)),
0, 1, (rng.uniform(10.f, 20.f)));
warpAffine(target_image, template_image, warpGround,
Size(200, 200), INTER_LINEAR + WARP_INVERSE_MAP);
break;
case MOTION_EUCLIDEAN:
angle = CV_PI / 30 + CV_PI * rng.uniform((double)-2.f, (double)2.f) / 180;
warpGround = (Mat_<float>(2, 3) << cos(angle), -sin(angle), (rng.uniform(10.f, 20.f)),
sin(angle), cos(angle), (rng.uniform(10.f, 20.f)));
warpAffine(target_image, template_image, warpGround,
Size(200, 200), INTER_LINEAR + WARP_INVERSE_MAP);
break;
case MOTION_AFFINE:
warpGround = (Mat_<float>(2, 3) << (1 - rng.uniform(-0.05f, 0.05f)),
(rng.uniform(-0.03f, 0.03f)), (rng.uniform(10.f, 20.f)),
(rng.uniform(-0.03f, 0.03f)), (1 - rng.uniform(-0.05f, 0.05f)),
(rng.uniform(10.f, 20.f)));
warpAffine(target_image, template_image, warpGround,
Size(200, 200), INTER_LINEAR + WARP_INVERSE_MAP);
break;
case MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY:
warpGround = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << (1 - rng.uniform(-0.05f, 0.05f)),
(rng.uniform(-0.03f, 0.03f)), (rng.uniform(10.f, 20.f)),
(rng.uniform(-0.03f, 0.03f)), (1 - rng.uniform(-0.05f, 0.05f)), (rng.uniform(10.f, 20.f)),
(rng.uniform(0.0001f, 0.0003f)), (rng.uniform(0.0001f, 0.0003f)), 1.f);
warpPerspective(target_image, template_image, warpGround,
Size(200, 200), INTER_LINEAR + WARP_INVERSE_MAP);
break;
}
}
const int warp_mode = mode_temp;
// initialize or load the warp matrix
Mat warp_matrix;
if (warpType == "homography")
warp_matrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_32F);
else
warp_matrix = Mat::eye(2, 3, CV_32F);
if (inWarpFile != "") {
int readflag = readWarp(inWarpFile, warp_matrix, warp_mode);
if ((!readflag) || warp_matrix.empty())
{
cerr << "-> Check warp initialization file" << endl << flush;
return -1;
}
}
else {
printf("\n ->Performance Warning: Identity warp ideally assumes images of "
"similar size. If the deformation is strong, the identity warp may not "
"be a good initialization. \n");
}
if (number_of_iterations > 200)
cout << "-> Warning: too many iterations " << endl;
if (warp_mode != MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY)
warp_matrix.rows = 2;
// start timing
const double tic_init = (double)getTickCount();
double cc = findTransformECC(template_image, target_image, warp_matrix, warp_mode,
TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT + TermCriteria::EPS,
number_of_iterations, termination_eps));
if (cc == -1)
{
cerr << "The execution was interrupted. The correlation value is going to be minimized." << endl;
cerr << "Check the warp initialization and/or the size of images." << endl << flush;
}
// end timing
const double toc_final = (double)getTickCount();
const double total_time = (toc_final - tic_init) / (getTickFrequency());
if (verbose) {
cout << "Alignment time (" << warpType << " transformation): "
<< total_time << " sec" << endl << flush;
// cout << "Final correlation: " << cc << endl << flush;
}
// save the final warp matrix
saveWarp(finalWarp, warp_matrix, warp_mode);
if (verbose) {
cout << "\nThe final warp has been saved in the file: " << finalWarp << endl << flush;
}
// save the final warped image
Mat warped_image = Mat(template_image.rows, template_image.cols, CV_32FC1);
if (warp_mode != MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY)
warpAffine(target_image, warped_image, warp_matrix, warped_image.size(),
INTER_LINEAR + WARP_INVERSE_MAP);
else
warpPerspective(target_image, warped_image, warp_matrix, warped_image.size(),
INTER_LINEAR + WARP_INVERSE_MAP);
//save the warped image
imwrite(warpedImFile, warped_image);
// display resulting images
if (verbose)
{
cout << "The warped image has been saved in the file: " << warpedImFile << endl << flush;
namedWindow("image", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
namedWindow("template", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
namedWindow("warped image", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
namedWindow("error (black: no error)", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
moveWindow("image", 20, 300);
moveWindow("template", 300, 300);
moveWindow("warped image", 600, 300);
moveWindow("error (black: no error)", 900, 300);
// draw boundaries of corresponding regions
Mat identity_matrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_32F);
draw_warped_roi(target_image, template_image.cols - 2, template_image.rows - 2, warp_matrix);
draw_warped_roi(template_image, template_image.cols - 2, template_image.rows - 2, identity_matrix);
Mat errorImage;
subtract(template_image, warped_image, errorImage);
double max_of_error;
minMaxLoc(errorImage, NULL, &max_of_error);
// show images
cout << "Press any key to exit the demo (you might need to click on the images before)." << endl << flush;
imshow("image", target_image);
waitKey(200);
imshow("template", template_image);
waitKey(200);
imshow("warped image", warped_image);
waitKey(200);
imshow("error (black: no error)", abs(errorImage) * 255 / max_of_error);
waitKey(0);
}
// done
return 0;
}
사용 OpenCV 함수
참조 링크
https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/d7/d1b/group__imgproc__misc.html#ga366aae45a6c1289b341d140839f18717

댓글남기기